Guitar Fills: What to Play When Your Singer Shuts Up
Learn how fills work in a variety of styles – from blues to pop to rock and metal.

A guitar solo may be the big moment in a song when you get to cut loose, but there are plenty of opportunities to support a song melodically throughout its performance – in fact, pretty much every time your lead singer shuts their mouth.
The key element here is the fill, an instrumental phrase played between vocal lines. Fills serve to provide filler – hence the name – in the moments when the song needs a melodic focal point, due to the absence of a vocal line. When placed effectively, fills can heighten a song’s intensity. For this reason, guitarists tend to fill more frequently as a song progresses, usually starting in the second verse.
To create an effective fill, you need to get in, play something hot and get out without detracting from the bigger picture – the song itself. Depending on the style, this means creating anything from a singable melody to a swaggering riff to a raunchy eruption of notes.
You’ll also need to be able to make smooth changes in volume and sound, adjusting your guitar, amp, and pedals as you shift quickly between rhythm and lead duties.
In this lesson you’ll learn how fills work in a variety of styles – from blues to pop to rock and metal. Once you’ve learned all these figures, try playing them in other keys and plugging them into different songs. Then try doing the same with some of your favorite players’ fills.
The Blues: Call-And-Response
The earliest guitar fills were played in the 1920s and 1930s by solo country-blues artists like Charley Patton, Son House, and Robert Johnson, who often punctuated their vocal phrases with two measures of improvised licks – bars 3–4, 7–8, and 11–12 of a 12-bar blues – creating a call-and-response effect between playing and singing.
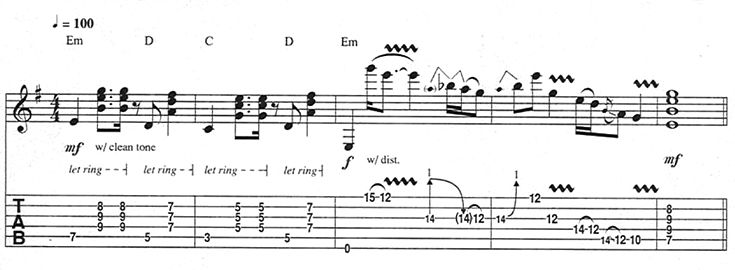
Later, electric bluesmen did the same, typically during the turnaround – the blues form’s last two bars – as shown in Figure 1. This turnaround is structured from A (A, C#, E) and D (D, F#, A) triads, with b3rd embellishments: each chord’s 3rd (C# and F#, respectively) is approached from a half step below.
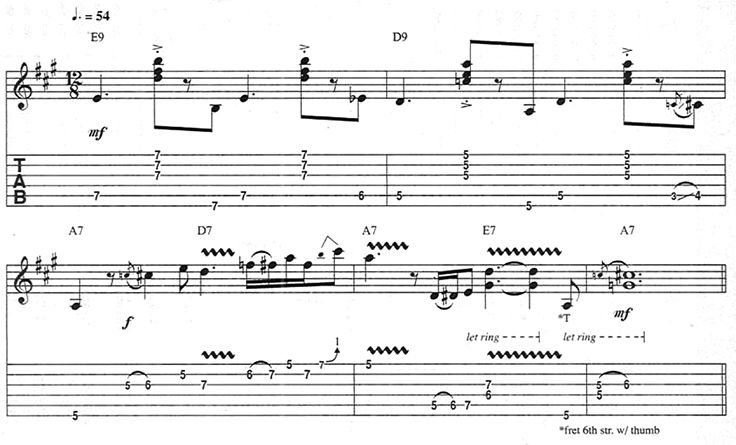

Play Figure 1 through a tube amp set with just a touch of gain, so that the opening chords sound slightly punchy. Pick harder during the single-note fill to make that lick stand out. To expand your vocabulary, seek out more blues fills and practice plugging them in after the first and second measures of a tune.
Classic Rock: Major And Minor Pentatonic Scales
Pioneering electric blues players like T-Bone Walker, B.B. King, and Albert King had a profound influence on the fills of classic-rock guitarists, namely Eric Clapton, Jimi Hendrix, Jimmy Page, Jeff Beck, and Carlos Santana. Clapton, in the power trio Cream, often had to alternate between rhythm and lead duties.
Check out Figure 2, which is inspired by the guitar parts during the verse of Cream’s “White Room.” Begin with your guitar’s volume knob rolled back (to reduce gain), then turn it up to 10 for the fill, or alternate between the clean and dirty channels of your amp using its footswitch.
George Harrison is generally regarded as the Beatles’ lead guitarist, but in the verses of “The Ballad of John and Yoko,” it was actually John Lennon who played the skillful E major pentatonic (E, F#, G#, B, C#) phrases.
In Figure 3, a riff is punctuated during non-vocal parts with assorted pre-bends and releases within the scale’s 9th (bar 2), 12th, and 17th positions (bar 3). Look to Harrison’s work on the verses of “Get Back" for similar explorations with the A major pentatonic scale (A, B, C#, E, F#).

In the 1970s, Fleetwood Mac’s Lindsey Buckingham, with his understated blues fills, emerged as a new kind of guitar hero.
A good example of his work can be found in the chorus of the group’s hit “Rhiannon,” in which Buckingham inserted crafty A minor pentatonic (A, C, D, E, G) fills between vocal phrases (Figure 4).
At the mezzo-forte marking (mf), turn on some subtle overdrive for a creamy lead tone. You might even try playing fingerstyle. Note that this fill is similar to Figure 2 – it’s just been revamped for a new key (A minor), tempo, and dynamic level.

Queen’s Brian May is a master of guitar orchestration. Against Freddie Mercury’s vocals, he would play smart harmony and counterpoint, resulting in a unique guitar-fill style.
For instance, in “Crazy Little Thing Called Love,” May darts between Mercury’s melodies with short licks, using the D minor pentatonic scale (D, F, G, A, C) over a D chord, and bending within a G triad (G, B, D), as in Figure 5.
Switch between channels of an amp set for two gain stages, or stomp on your overdrive pedal to make these brief fills jump out.

R&B/Pop: Double-Stops And Chord Partials
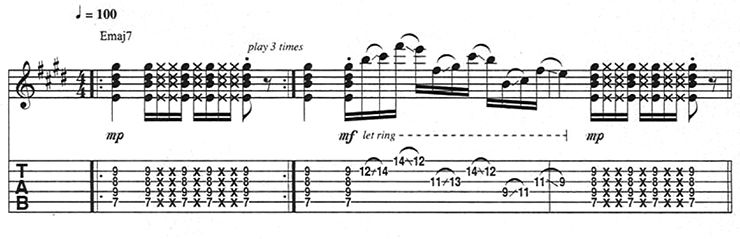
R&B and pop guitarists typically make fills with double-stops and chord partials from pentatonic scales. For example, in “Little Wing,” over an Em - G - Am progression, Jimi Hendrix plays E minor pentatonic (E, G, A, B, D), G major pentatonic (G, A, B, D, E), A minor pentatonic (A, C, D, E, G), and E minor pentatonic fills (Figure 6).
After playing the chord on the downbeat and letting it ring for a couple of beats, Hendrix delivers fills at the end of each measure, usually while taking a breath between vocal phrases.
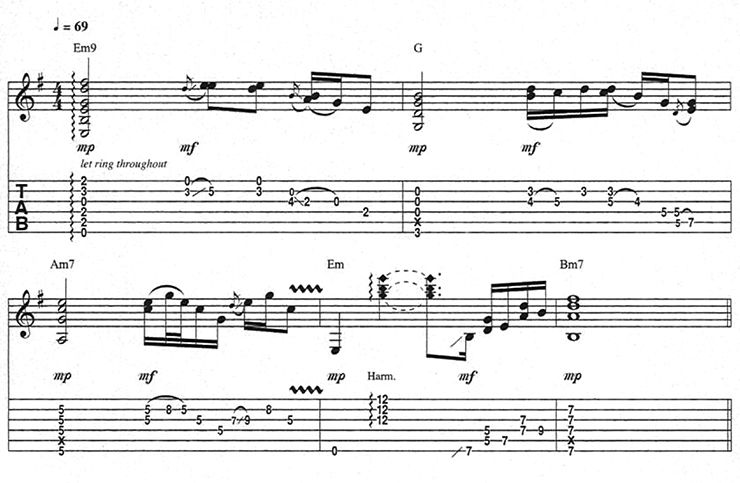

Most often, for every two strings played together, the higher note rings against a hammered-on embellishment on the lower string.
These fills are indebted to R&B guitar greats like Curtis Mayfield and Steve Cropper and are a studio musician’s bread and butter – invaluable when it comes to improvising appropriate pop and light-rock fills.
Figure 7 illustrates an R&B-flavored lick in which the E major pentatonic scale (E, F#, G#, B, C#) is used in sliding 4ths to punctuate a funky Emaj7 vamp. Something similar happens in Marvin Gaye’s “What’s Goin’ On.”
In E major pentatonic, 4ths occur between F# and B, G#, and C#, B, and E and C# and F#.
Depending on the string pair used, these figures require either a 1st-string barre (strings 1–2, 3–4, 4–5 and 5-6) or the use of the 1st and 2nd fingers (strings 2–3). Pick the lower note of each dyad and slide it up to the next scale degree, then pick the higher string and slide back down.
Hard Rock And Metal: Cool Tricks And Blazing Licks
In hard rock songs by groups like Journey, Boston, and Toto, the guitar shares the limelight with the vocals. Melodic pickers Neal Schon, Tom Scholz, and Steve Lukather rise above their bands’ predominant keyboard textures with plenty of tasty fills.
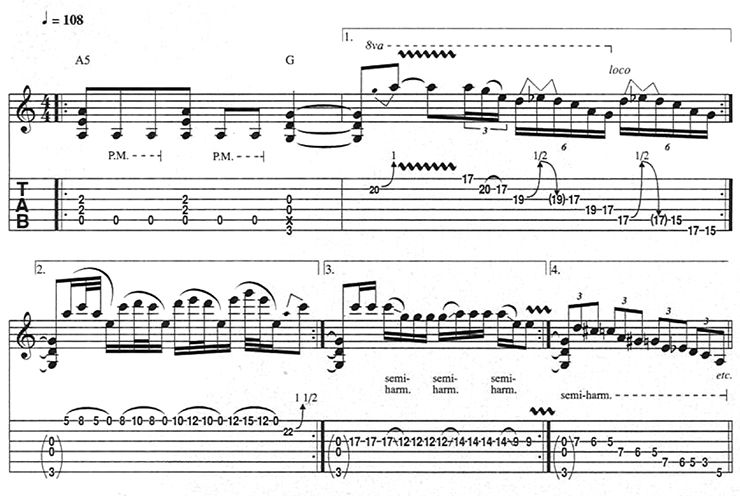
Figure 8 is similar to Journey’s “Faithfully.” For the sweet B major pentatonic (B, C#, D#, F#, G#) phrase in bar 2, stomp on your distortion pedal as you switch from your bridge to neck pickup.

Metal players like Randy Rhoads, Zakk Wylde, and Dimebag Darrell often punctuate a power-chord riff with a blazing pentatonic lick (Figure 9).
To cop their moves, it helps to have an assortment of minor-pentatonic tricks up your sleeve – everything from open-string pull-off licks (Figure 9, bar 3) to sawtooth sequences (bar 4) to licks involving chromatic passing tones (notes outside of the key used to connect diatonic pitches, as shown in bar 5).
For the slight pinch harmonics (indicated as “semi-harm.”) in measures 4 and 5, lightly touch the string with the outer edge of your pick-hand’s thumb as you pick, producing a squealing overtone.
To hear similarly pyrotechnical fills in context, consult any of the live G3 recordings, Ozzy Osbourne’s’ Tribute (with Randy Rhoads) and Live at the Budokan (with Zakk Wylde), as well as Guns N’ Roses Live Era: ‘87–’93.
Get The Pick Newsletter
All the latest guitar news, interviews, lessons, reviews, deals and more, direct to your inbox!
Guitar Player is the world’s most comprehensive, trusted and insightful guitar publication for passionate guitarists and active musicians of all ages. Guitar Player magazine is published 13 times a year in print and digital formats. The magazine was established in 1967 and is the world's oldest guitar magazine. When "Guitar Player Staff" is credited as the author, it's usually because more than one author on the team has created the story.
“Write for five minutes a day. I mean, who can’t manage that?” Mike Stern's top five guitar tips include one simple fix to help you develop your personal guitar style
"It’s like you’re making a statement. And you never know where it’ll lead." Pete Thorn shares the tip that convinced Joe Satriani he was the right guitarist for the SatchVai Band










